EU lawmakers enact landmark AI act, regulating AI development and risks
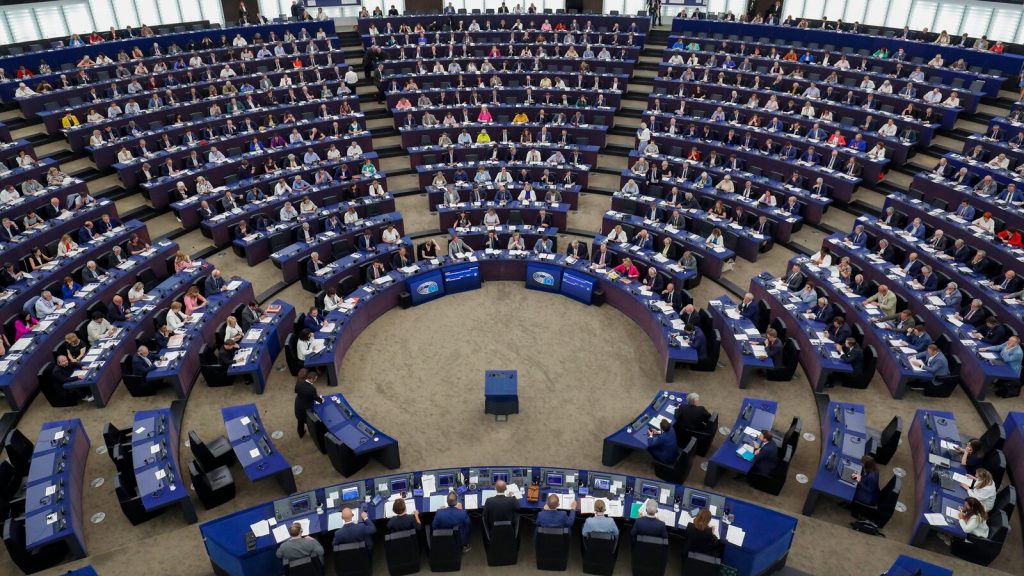

European Union lawmakers have reached an agreement on a significant artificial intelligence law, known as the AI Act, marking one of the world’s earliest comprehensive regulations in this field.
The legislation aims to foster AI development while mitigating associated risks, specifically banning AI practices deemed hazardous to people’s safety and rights.
Roberta Metsola, the European Parliament president, praised the law as a “balanced and human-centered approach,” expected to set global standards for years.
The AI Act categorizes AI uses by risk level, imposing stricter regulations on higher-risk applications.
Notably, the law prohibits the riskiest AI uses, including systems targeting vulnerable groups, biometric identification in law enforcement, and AI employing manipulative techniques.
Lower-risk AI systems, like chatbots such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT, face new transparency requirements under the legislation.
Thierry Breton, the EU Commissioner for Internal Market, highlighted the AI Act’s potential to propel EU startups and researchers into leadership positions globally.
AI technology, particularly with the emergence of OpenAI’s ChatGPT in November 2022, rapidly gained traction and sparked a surge in generative AI’s popularity, triggering an AI competition across various sectors.
Its disruptive impact extended beyond tech, affecting education, art, music, and media industries, with controversies arising.
Companies behind AI tech faced challenges too. OpenAI witnessed internal disruptions, notably with CEO Sam Altman briefly leaving and returning under unclear circumstances, causing speculation and uncertainty.
Overall, the AI Act represents a pioneering step in regulating AI, aiming to balance innovation with safeguarding against potential risks associated with its widespread use.
Source-CNN





